Issue No. 3: Vietnam Supply Chain. Insights on Current Challenges

Over the past few years, the supply chain in Vietnam has contributed to the production and business activities of many enterprises as well as the entire operation of the economy. The flow of goods and services circulating in the market is increasingly rich, improving in quality, and satisfying customers’ needs.
However, the supply chain in Vietnam is still at a low level of development, which has not fully promoted the function of integrating economic organizations and activities in the national economic system. Moreover, the spread of COVID-19 has disrupted the way global supply chains operate, making it difficult for businesses in every country, including Vietnam to model and assess risks. The supply chain practice in the past will no longer be favorable to support the future marketplace.
In this article, we’ll take a look at the top supply chain issues, showing the results, limitations, and causes across the whole system.
The impact of global unrest
The global unrest poses the largest risks to Vietnamese manufacturing. Although Vietnam is a country that imports raw materials to manufacture export goods, the input is heavily dependent on foreign countries, causing difficulties and a dramatic increase in prices.
After Russia invaded Ukraine, Hanoi forewarned of downstream shocks to supplies, which were already suffering from China’s decision to tighten its land border with Vietnam in December. Added to that now is a COVID shutdown in China that includes the world’s busiest port, in Shanghai.
As a result of China adopting tiered COVID measures, enterprises in Vietnam are struggling to manage supply chain breakages, especially the raw material supply and exports because China usually supplies a large number of materials used by many industries in Vietnam for production.
This is not just holding down manufacturing, some businesses are struggling to complete their export orders. If raw materials cannot be imported for production, the company’s order will not be delivered on time, causing the contract to be canceled by the customers.
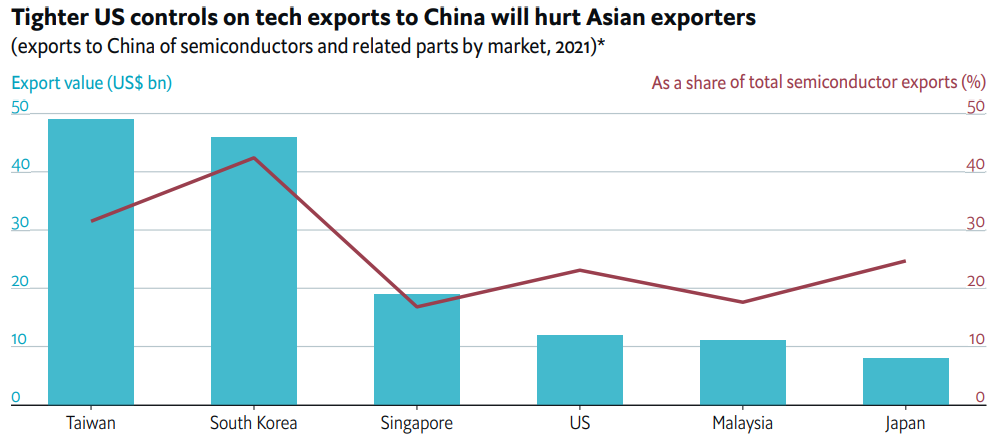
Exports of agricultural produce to China – one of the main consumers of Vietnamese produce, have also been negatively impacted by stricter customs checks and procedures. Week-long delays and even turns aways occur at entrance gates for export containers. Fruit and vegetable exports to China decreased by 25% year over year in the first quarter of 2022.
The global unrest poses the largest risks to Vietnamese manufacturing. Although Vietnam is a country that imports raw materials to manufacture export goods, the input is heavily dependent on foreign countries, causing difficulties and a dramatic increase in prices.
After Russia invaded Ukraine, Hanoi forewarned of downstream shocks to supplies, which were already suffering from China’s decision to tighten its land border with Vietnam in December. Added to that now is a COVID shutdown in China that includes the world’s busiest port, in Shanghai.
As a result of China adopting tiered COVID measures, enterprises in Vietnam are struggling to manage supply chain breakages, especially the raw material supply and exports because China usually supplies a large number of materials used by many industries in Vietnam for production.
This is not just holding down manufacturing, some businesses are struggling to complete their export orders. If raw materials cannot be imported for production, the company’s order will not be delivered on time, causing the contract to be canceled by the customers.
Exports of agricultural produce to China – one of the main consumers of Vietnamese produce, have also been negatively impacted by stricter customs checks and procedures. Week-long delays and even turns aways occur at entrance gates for export containers. Fruit and vegetable exports to China decreased by 25% year over year in the first quarter of 2022.
Current challenges throughout the 4 stages of the supply chain in Vietnam
According to a survey conducted by KPMG (2021), there are a few of the major challenges highlighted across 4 stages of the supply chain for Vietnam: Plan, Source, Make and Deliver.
Plan – Lack of long-term planning
Strategic and integrated planning is essential for maximizing the effectiveness of supply chains because it ensures the alignment between the supply chain operations and the business direction. However, most companies are spending efforts on short-term planning with a lack of accuracy in the forecasting process and real-time visibility of cost, service level, inventory, etc. on the end-to-end supply chain.
Another key issue is that each department inside supply chains tends to pursue its priorities rather than following a unified course. As a result, we can see that even when the organizational workforce appears to be occupied by planning activities, the businesses are still having repetitive failures with uneven demand and supply, slow-moving inventory, and lost revenue.
Source – Lack of local supply base
In this stage, companies need to select suppliers to deliver the items and services they require to develop their products. However, most companies struggle with the uncertainty of supplier delivery, and the lack of a qualified supply base for alternative sources, which disrupts production and distribution.
One of the significant root causes of those pain points is that companies are exerting all effort to control operational procurement but not investing in proper procurement and category strategies. Procurement is focused too much on price instead of service quality. Category management, supplier relationships, and risk management are among the top areas that can significantly contribute value to generating cost savings and enhancing supply stability but are currently underestimated.
Make – Low manufacturing capability
Manufacturing is the backbone of the business, and production efficiency has a big impact on the company’s performance. However, companies are still having trouble figuring out how to increase their manufacturing capacity. Changeovers occur frequently because supply planning and production scheduling are not well integrated.
Lack of maintenance or inadequate maintenance is leading to frequent asset breakdowns and unexpected shutdowns. Inefficient recruitment process and talent shortage also cause difficulties in improving production quality. These top concerns demand a holistic strategy to reinforce shop floor practices and improve manufacturing performance.
Delivery – Challenges for the delivery stage
The delivery stage is often referred as the logistics phase, where the products are delivered to the customer at the specified location by the supplier.
Poor infrastructure is one of the main problems that the logistics sector is currently facing. Domestic businesses have not fully established a multimodal transport corridor, while the demand for high-quality transshipment is still rising. The operation efficiency of the Vietnamese seaport is very low due to the lack of proper infrastructure.
The two other major constraints for the delivery stage are cost-to-serve management and warehouse management. Companies struggle with compiling and analyzing data to identify specific areas for improvement even though they are aware of the value of cost-to-serve visibility.
Warehouse leasing supply is currently not enough to fulfill demand due to limited floor space. The construction of warehouses and depots in three regions, along with the system of wharves, roads, and warehouses, is still in its early stages and is not complete, so it only meets the needs for import and export rather than domestic demand, particularly demand for E-Logistics.
Therefore, optimization of warehouse operations is also a potential area for improvement that most businesses need to put serious effort into it.

Other existing concerns
Manpower
According to statistics from the Vietnam Logistics Business Association (VLA), foreign companies account for 80% of Vietnam`s logistics market. Local firms which offer separate services and small segments find it difficult to compete with foreign counterparts who have access to much more capital and labor.
In Vietnam, logistics human resources are deficient in both quantity and quality, especially highly qualified personnel at the managerial level and logistics experts who are familiar with national laws to apply and use them effectively in their work.
Technology and digital solutions
Although logistics enterprises have an awareness in applying technology to their business activities, they are still slow to adapt to the digital transition and are out of touch with current technology.
While rising supply chain technology trends like AI, Big Data, Internet of Things (IoT), digital twins, and blockchain are taken into consideration in more mature markets, supply chain leaders in Vietnam appear to place a greater emphasis on getting the fundamentals right.
Expenses for logistics services
The COVID-19 pandemic disrupted the world’s supply chain, and at the same time, freight costs shot up significantly, particularly on routes to Europe and America. Mr. Dang Dinh Long, Director of Mega A Trading Investment Joint Stock Company, reflected that after several instances of port closures in China, the freight rates immediately increased by 15%-20%.
Recently, the conflict between Russia and Ukraine has pushed up the price of oil and many kinds of raw materials and fuel, turning import and export costs a burden beyond the tolerance of many businesses.
High freight rates, which are forecast to remain high in 2023, are one of the biggest challenges for businesses. The fact that Vietnam’s logistics costs are much higher than the global average causes an increase in the cost of goods, reducing its competitive advantages compared to other countries in the region.

Vietnam’s economic integration with the rest of the world is progressing, and the scale of the market for logistics services is growing. Therefore, it is critical for Vietnamese enterprises to develop strategies to minimize supply chain disruptions in the face of global uncertainty and take advantage of overseas investment.
Author Karlheinz Zuerl
CEO of GTEC German Technology & Engineering Cooperation
Diplomatic Council Trusted Member
More solutions you will find on our website and in our eBook shop.
If any questions and wishes, please contact me for a Zoom meeting in order to dig into details together, to get your benefit out of our knowledge.
- My Blogs at https://www.linkedin.com/in/karlheinz-zuerl-04859b2b/recent-activity/posts/
- My profile at UI: www.unitedinterim.com/interim-manager/automotive-business-china-asien
Mobile: +86 134 8243 8080
Don´t wait, Asia is fast.